One of the common terms used in the field of software, website, and product development is UI and UX design. Most of you have probably heard about it. Many people also consider both UI and UX the same thing, or at least interchangeable terms. However, there are many differences between the two regarding their functions and purpose in the development of products. And in this guide, we’ll explain in detail what UI and UX are, their differences, and even a brief overview of the steps involved in UI and UX design.
Let’s start with a basic explanation of UI and UX.
What is UI?
UI is the abbreviation of User Interface. It’s that aspect of a product that users can see and interact with. It focuses on the visual or aesthetic elements of the product and some of its functions. Here are some examples:
- For a website, UI is the website's look – the colors, placement of different menus and buttons, the design of each webpage, etc. Other elements of a website UI include forms, chat boxes, and even touch elements for users who browse the website on touch-enabled devices like mobile and tablets.
- For gadgets such as mobile, PCs, and laptops, the UI involves input and output hardware such as display, keyboard, and mouse and arrangement of various settings, buttons, and icons.
- For mobile and computer applications, the UI is the app's controls, menus, and settings.
- In smart devices like TVs or household appliances, UI has many aspects such as the control panel, buttons, and digital display.
Overall, the purpose of UI is to improve the overall look of the product. It makes things self-explanatory for users when interacting with the product. Users should be able to access all information and functionalities easily since the accessibility of different components is an essential fact.
What is UX?
UX stands for User Experience, and it goes much beyond just the display and looks. UX deals with every aspect that affects people's experience. Considering the same cases as above, here are some examples of what makes up the UX of a product.
- For websites, the UX can include numerous aspects such as loading speed, navigation, and even the website's content. After all, quality content that offers value to users will improve their experience on the site.
- For mobiles, PCs, and laptops, the UX is determined by factors such as processing speed, boot time, multitasking ability, and how easy it is to use different device functions.
- For mobile and computer applications, the UX deals with all aspects that affect the experience of a user on the app, such as:
- Guides and tutorials for new users on the app to explain the basic functions
- The usability of the app, means how easy and convenient it is for someone to use the app.
- If it’s an online application, then connectivity issues must also be considered. If the app can still function even when the internet speed fluctuates, then the users will certainly enjoy smooth and uninterrupted usage.
- For smart devices and appliances, the UX involves factors such as size, portability, usability, and even electricity consumption.
These are just some cases of what influences the UX of these products. UX is a vast field that involves just about anything that will affect the final experience of a user. UI is a part of the overall UX of a product because the user interface is also one out of many other things that will determine the user experience. Therefore, UI itself comes under the bigger umbrella of UX.
Difference between UI and UX
After explaining UI and UX, you might have probably realized that they are interconnected aspects of product development. It’s not possible to have good UX with bad UI, or even the other way round.
Let’s say all aspects of a product, such as a usability, accessibility, and functionality are excellent. But if it doesn’t have a great user interface, the overall user experience will go down. On the other hand, if a product has an amazing user interface but falls short on other areas like usability and functionality, users will not enjoy it.
If they are so closely related, why do we need to focus on the differences between them? The reason is that even though they are interconnected, they are still two individual aspects of product development. There will be individuals and teams who focus solely on UI and others who work on UX. While UI and UX teams will collaborate, they both have their own set of responsibilities and goals. That is why it’s crucial to understand the difference between both.
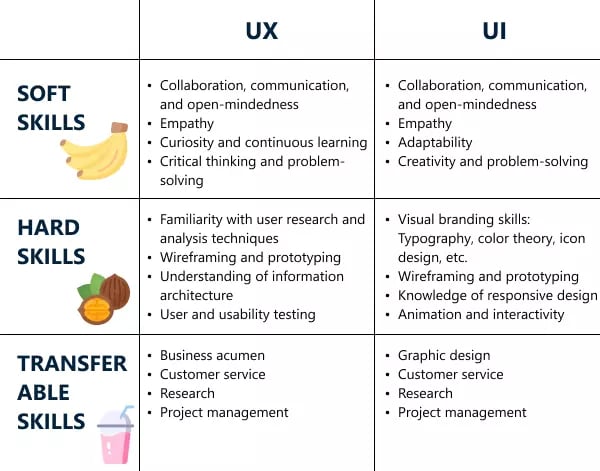
UX and UI can be differentiated through their roles and their design or implementation.
- The Role of UI vs. UX
We already explained the roles of both UI and UX.
- UI design deals with the graphical and visual elements of a product, as well as the human-machine interface that lets users interact with the product.
- UX design deals with the journey and overall experience of users. It is a much wider and bigger aspect of product development that encompasses UI as well.
- The Implementation/Design of UI vs. UX
The next important difference between UI and UX lies in how they are implemented during product development.
Let us consider an analogy – in a car, there are many components like the engine and internal systems which determine the performance of the car but can’t be seen directly. Then there’s the look and design of the car, which is immediately visible.
During the manufacturing process, the engines and systems are designed to have excellent performance and drive smoothly in all conditions. Once that is done, the outer components will be added on top of the internal systems to make the car look sleek and stylish. That is also the case with UI and UX design. First, the UX design team will lay out the foundations of the product so that it will offer a high-quality user experience.
UX design process
The process of UX design can be divided into two stages.
The first part is visualization. It begins with research about the target audience and how the product can solve their problem. Then more research is done on what features the audience would enjoy in the product. The next step is to create a structure to integrate all those features to make them easy to access and use.
The second part is development. The features and functionalities discussed in the previous stage are systematically added to the product in this stage. Each feature is tried and tested to ensure the functionality and whether it can easily be understood and operated by the target audience.
UI design process
In the UX design process, the structures, features, and content of the product are determined. Then it’s time to add a layer of the visual interface that will allow users to interact with the features and content. This is what UI design is all about. The process of UI design can be divided into three stages:
The first part is functionality. In this stage, the designers have to ensure that all elements of the UI, such as icons, buttons, and control layouts work as intended and connect with the respective features.
The second part is accessibility. In this stage, the designers work on the appropriate arrangement of all UI elements so that everything can be quickly and easily accessed by users. The interface must be easy to navigate with minimum effort from the user. It must also be self-explanatory so that users will understand what the buttons and icons do or represent easily.
The final part is the aesthetic design. Now that all the UI elements work smoothly and are easily accessible, it’s time to make them look good. So in the final stage, the designers must come up with a neat and aesthetically pleasing design for the user interface.
Summery
Understanding the role of UI and UX design and their differences is important for developers so that they can focus on each aspect properly to create an excellent product. This is also essential for designers and for those who are looking to build a career in UI or UX designs. But it’s also equally important for general consumers and users to better evaluate a product, provide feedback to the developers, and make better decisions on whether a product is worth their time and money.
Build unique products, boost device performance
See why emteria is the chosen Android™ customization & management platform for OEM solution builders — and what it can do for your team and customers.